24-unit apartment building plans encompass a multifaceted process, requiring meticulous consideration of architectural styles, building materials, site selection, and financial projections. This comprehensive overview details the key aspects involved in designing, constructing, and managing such a project, ensuring both functional efficiency and profitability.
The document explores various architectural styles, from modern to traditional, evaluating their suitability for a 24-unit complex. It analyzes the cost implications of different building materials, factoring in long-term maintenance requirements. Furthermore, the document assesses the crucial role of sustainable design elements in reducing environmental impact and optimizing energy efficiency.
Building Design Considerations

Planning a 24-unit apartment building requires careful consideration of architectural style, materials, sustainability, space optimization, accessibility, and fire safety. A well-designed building not only meets the needs of residents but also contributes to a positive living environment and long-term building performance. These considerations are crucial for achieving a functional, aesthetically pleasing, and sustainable structure.Careful planning in these areas is essential for achieving a high-quality building that addresses the needs of its future residents.
This involves evaluating various architectural styles, material choices, and spatial arrangements to ensure the building meets modern standards and anticipates future needs.
Architectural Styles
Different architectural styles offer various aesthetic qualities and structural possibilities. Modern styles, characterized by clean lines and open spaces, are often preferred for their contemporary appeal. Traditional styles, such as Craftsman or Victorian, might offer a cozy and inviting ambiance. The chosen style should be harmonious with the surrounding environment and the desired aesthetic of the project.
Considerations include local building codes, zoning regulations, and the target demographic.
Building Materials
Building materials significantly impact both the initial cost and the long-term maintenance of the building. Concrete, a common material, is relatively inexpensive but requires substantial reinforcement for high-rise structures. Brick offers a classic aesthetic and good insulation, but its cost can be higher than other options. Steel provides strength and allows for flexibility in design but is susceptible to corrosion.
The selection of materials should consider the balance between cost, durability, and aesthetic appeal.
Sustainable Design Elements, 24-unit apartment building plans
Incorporating sustainable design elements is crucial for reducing the environmental impact of the building. Solar panels on the roof can generate renewable energy, reducing reliance on the grid. Energy-efficient windows and insulation can minimize heating and cooling costs. Rainwater harvesting systems can collect and store rainwater for irrigation, reducing water consumption. Sustainable practices reduce the building’s carbon footprint and contribute to a healthier environment.
While the 24-unit apartment building plans promise increased housing density, a critical perspective necessitates considering the local market. The availability of comparable housing options, such as those in Berrien Springs, Michigan, exemplified by Berrien Springs homes for sale , needs careful analysis. Ultimately, the success of the 24-unit plans hinges on aligning with current housing demand and local market realities.
Layout Options for Maximizing Space and Natural Light
Layout options significantly impact the livability of the apartments. Open floor plans can maximize space and create a sense of spaciousness. Strategic placement of windows maximizes natural light and ventilation. Balconies or patios provide outdoor living space. The layout must consider traffic flow, privacy, and accessibility.
Accessibility for People with Disabilities
The building should be designed to comply with accessibility guidelines. Wide doorways, ramps, and accessible restrooms are essential. Elevators and ramps should be strategically placed for convenient access throughout the building. This commitment to accessibility benefits everyone.
Fire Safety Regulations
Fire safety is paramount. Sprinkler systems, fire alarms, and emergency exits are critical components. The building design should incorporate fire-resistant materials and comply with local fire codes. Regular fire drills and training for residents are also essential.
Building Materials Comparison
| Material | Pros | Cons | Energy Efficiency | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concrete | Strong, durable, readily available | Heavy, may require significant reinforcement | Moderate | Low to Medium |
| Brick | Aesthetically pleasing, good insulation | Can be more expensive than concrete, heavier | Good | Medium to High |
| Steel | Strong, versatile, allows for complex designs | Susceptible to corrosion, requires maintenance | Moderate | Medium to High |
| Wood | Aesthetically appealing, relatively light | Susceptible to rot, fire, insect damage | Moderate | Low to Medium |
| Aluminum | Lightweight, corrosion resistant, good for curtain walls | May not be as strong as steel, can be expensive | Moderate | High |
Unit Specifications and Amenities
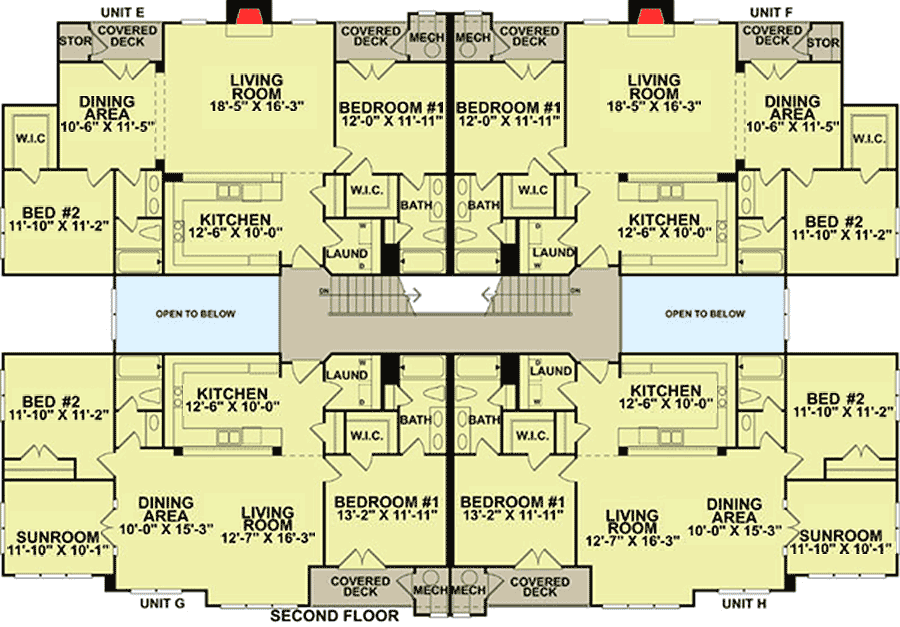
The design of the 24-unit apartment building hinges on creating a comfortable and desirable living experience for residents. This involves careful consideration of unit sizes, layouts, and amenities, along with the integration of modern technology and thoughtful design elements that prioritize privacy and quiet enjoyment. Optimizing these aspects ensures the building’s appeal to prospective tenants and long-term sustainability.The unit specifications must balance functionality with aesthetic appeal, accommodating various needs and budgets.
Essential amenities should be carefully chosen to enhance the overall living experience and attract residents. The inclusion of modern technologies and smart home features further elevates the living experience and offers convenience.
Ideal Unit Sizes and Layouts
Unit layouts are crucial for maximizing space and functionality while accommodating diverse needs. Different unit types, such as studios, one-bedroom, and two-bedroom apartments, will require varying degrees of space allocation. A studio apartment, for example, will benefit from a thoughtfully designed open-plan layout, optimizing space utilization and flexibility. One-bedroom units should prioritize a separation between living and sleeping areas.
Two-bedroom units will need to accommodate both bedrooms, a living area, and a kitchen/dining area, along with adequate storage space.
Essential Building Amenities
Essential amenities are key for creating a desirable living environment. These amenities will improve the quality of life for the residents and elevate the building’s overall appeal. The inclusion of a well-equipped fitness center, a secure parking area, and a landscaped common area will enhance the living experience. Incorporating a dedicated community room, a rooftop terrace, or a package receiving area will further increase the appeal and value of the building.
Privacy and Quiet Enjoyment
Careful design considerations are vital for ensuring privacy and quiet enjoyment for all residents. Soundproofing measures, strategically placed sound barriers, and careful planning of unit layouts can help minimize noise transfer between units. Adequate room separation within units, along with well-designed hallways and common areas, will contribute to the overall sense of peace and tranquility. Noise control measures are paramount to ensuring residents can enjoy their space without disturbance.
Incorporating Modern Technologies and Smart Home Features
The incorporation of modern technologies enhances the convenience and efficiency of daily living. Smart home features, such as automated lighting, temperature control, and security systems, can improve the comfort and safety of residents. Integration of smart locks, keyless entry, and automated appliances contribute to a more efficient and convenient lifestyle.
Kitchen and Bathroom Designs
Kitchen and bathroom designs play a critical role in maximizing space and functionality. Open-concept kitchens, maximizing natural light and visibility, and incorporation of high-quality appliances can enhance the cooking experience. Compact yet functional bathroom designs are critical, especially in smaller unit types. The installation of energy-efficient appliances and fixtures will lower water and energy consumption.
Unit Types, Sizes, and Costs
| Unit Type | Size (sq ft) | Estimated Cost ||—|—|—|| Studio | 400-500 | $1,800 – $2,200 || One-Bedroom | 600-800 | $2,200 – $2,800 || Two-Bedroom | 900-1200 | $2,800 – $3,500 |
Storage Solutions
Efficient storage solutions are essential for maximizing space and minimizing clutter. Built-in cabinets, drawers, and shelves can effectively utilize vertical space. Multi-functional furniture pieces, such as storage ottomans and beds with built-in drawers, can maximize storage capacity. Utilizing wall space for shelving and maximizing closet space will contribute to a clutter-free and organized living space.
Site Planning and Zoning Regulations
Careful site selection is crucial for the success of a 24-unit apartment building. A well-chosen location considers factors such as accessibility, infrastructure, and the surrounding community. This impacts the building’s market value, tenant satisfaction, and long-term profitability. The site’s suitability must also align with local zoning regulations, influencing the building’s design and size.The proper understanding and compliance with local zoning ordinances are vital to ensure a smooth project development process.
Failing to adhere to these regulations can lead to delays, cost overruns, and even project termination. Careful planning from the outset, including the evaluation of site challenges and the implementation of appropriate solutions, is essential for a successful project.
While 24-unit apartment building plans often prioritize efficiency and affordability, a comparative analysis with the market standards of luxury developments like those found in the West Village, exemplified by west village luxury apartments nyc , reveals critical considerations. The high-end amenities and design features demanded by this segment of the market suggest that even a modest 24-unit project needs to carefully balance its scale with aspirational design elements to maintain its competitive edge in the current real estate landscape.
Site Selection Considerations
The choice of a suitable site significantly influences the project’s success. A prime location offers better accessibility to amenities, employment centers, and public transportation, which attract tenants. Proximity to schools, parks, and recreational facilities also contributes to a desirable living environment. Understanding the demographics of the surrounding community helps to tailor the building’s amenities and features to meet the needs of potential residents.
- Proximity to Amenities: Consider the distance to shops, restaurants, parks, and other community facilities. Close proximity often translates to higher tenant satisfaction and rental rates.
- Accessibility and Transportation: Evaluate the ease of access to public transportation, major roads, and highways. Proximity to public transportation reduces reliance on personal vehicles, which can be a significant factor for tenants.
- Infrastructure: Assess the availability of utilities, such as water, electricity, and sewer lines. Adequate infrastructure ensures the smooth operation of the building and minimizes potential future problems.
- Environmental Factors: Evaluate the site’s environmental conditions, including noise levels, air quality, and proximity to industrial areas. A quiet and healthy environment enhances the appeal of the building.
- Zoning Regulations: Familiarize yourself with the local zoning ordinances and their restrictions on building height, density, and setbacks. Understanding these regulations helps to avoid potential issues later.
- Community Acceptance: Assess the potential for community opposition. A positive reception from residents can streamline the approval process.
Zoning Regulations and Their Impact
Zoning regulations dictate permissible building characteristics within specific areas. These regulations often include building height, density, setback requirements, parking minimums, and allowed building uses. Non-compliance can result in costly legal battles and delays.
- Building Height and Density: Zoning ordinances specify the maximum permissible building height and the maximum number of units allowed per acre. These regulations significantly impact the building’s design and potential size.
- Setback Requirements: Setbacks dictate the minimum distance between the building and property lines. These requirements are designed to ensure adequate light, air, and visibility for surrounding properties.
- Parking Requirements: Local regulations specify the minimum number of parking spaces required per unit. These requirements influence the design and layout of the building, often requiring dedicated parking areas or garages.
- Allowed Building Uses: Zoning ordinances may restrict the types of buildings that can be constructed in specific areas. This might include limitations on residential units, commercial spaces, or mixed-use buildings.
Addressing Site Challenges
- Slopes: Buildings on sloped sites require careful design to ensure stability and accessibility. Grading and retaining walls might be necessary. Design features like ramps or stairways should be incorporated.
- Limited Space: Limited space necessitates creative building designs that maximize the use of available area. Multi-level parking or compact unit layouts might be necessary. Innovative architectural solutions can help to overcome these challenges.
Parking Requirements
Parking requirements vary based on local zoning regulations. These regulations impact the design and layout of the building, potentially requiring dedicated parking areas or garages. Understanding these requirements is crucial for the project’s feasibility.
Permitting and Approvals
Obtaining necessary permits and approvals is a critical step in the building process. This involves submitting comprehensive plans and documentation to the relevant local authorities. Compliance with all regulations is essential.
Zoning Regulations Table
| Zoning Regulation | Potential Implications on Building Design | Potential Implications on Building Size |
|---|---|---|
| Building Height | Architectural design, material choices, elevator placement | Number of floors, overall height |
| Density | Unit layout, shared amenities | Total number of units, building footprint |
| Setbacks | Building footprint, exterior design | Reduced building area, potential for setbacks |
| Parking Requirements | Parking lot design, garage size | Reduced usable space, impact on building’s footprint |
Financial Projections and Cost Estimation: 24-unit Apartment Building Plans
Financial projections are crucial for the successful development of the 24-unit apartment building. A thorough understanding of anticipated costs, funding sources, and potential returns is essential to securing the project’s viability and attracting investors. This section details the financial planning strategy, outlining cost breakdowns, funding options, and cost-saving measures to maximize profitability.
Cost Breakdown by Project Phase
Accurate cost estimation is fundamental to project success. A comprehensive breakdown of costs across different project phases, from land acquisition to ongoing maintenance, allows for effective budget management and risk mitigation.
- Land Acquisition: This phase encompasses the purchase of the land and any associated legal fees. Factors such as location, zoning regulations, and market conditions significantly influence the cost of land acquisition. For example, prime locations often command higher prices, and navigating complex zoning processes can add to the overall expenses. Accurate appraisals and due diligence are paramount to ensuring a fair price and minimizing potential disputes.
- Design and Permits: This phase involves architectural design, engineering plans, and securing necessary permits. Professional fees for architects, engineers, and legal counsel contribute to these costs. Detailed project plans, including site layout and building specifications, should be meticulously prepared to avoid costly revisions and delays during construction.
- Construction: This phase includes material procurement, labor costs, and construction management. The cost of materials (concrete, steel, lumber) varies depending on market conditions and availability. Properly estimating labor costs and project timelines are vital to preventing cost overruns. Consider incorporating contingency funds for unexpected material price fluctuations or unforeseen construction challenges.
- Interior Finishes: This includes fixtures, appliances, and interior design elements. The choice of materials and level of sophistication in the interiors directly impacts the costs. Prioritizing quality without compromising budget constraints is key.
- Financing Costs: Interest payments, loan fees, and other financing charges need to be factored into the overall project budget. Different financing options have varying interest rates and repayment schedules, impacting the project’s financial viability.
- Ongoing Maintenance: This phase accounts for routine repairs, maintenance of common areas, and potential replacements. Adequate reserves for future maintenance are crucial to avoid significant unexpected costs.
Funding Options
Securing sufficient funding is a crucial aspect of project development.
- Bank Loans: Traditional bank loans are a common source of funding, offering fixed interest rates and predictable repayment schedules. Loan approval often hinges on the strength of the project’s financial projections and the applicant’s creditworthiness.
- Equity Financing: Investors or partners can provide equity capital in exchange for a stake in the project. Equity financing can offer flexibility but involves negotiating ownership structures and potential conflicts of interest.
- Government Grants: Local or state government programs may offer grants or subsidies to encourage affordable housing or sustainable development. Applicants need to meet specific eligibility criteria to qualify.
- Private Investments: Individual investors or venture capital firms may provide funding in exchange for a return on investment. Identifying potential investors requires a clear understanding of the project’s financial viability and market appeal.
Construction Cost Estimation Methods
Various methods are available for estimating construction costs.
- Detailed Cost Breakdown: This method involves itemizing all materials, labor, and other direct costs. It requires detailed plans and specifications, and is time-consuming but provides a precise estimate.
- Unit Cost Method: This method uses historical data and unit costs to estimate total construction costs. It is quicker than a detailed breakdown but may not account for specific site conditions.
- Quantity Surveying: This method involves measuring quantities of materials required for the project, then using unit costs to determine the total construction cost. This approach is effective in assessing the feasibility of a project and estimating the budget.
Cost-Saving Measures
Implementing cost-saving measures can significantly impact the project’s overall budget.
- Efficient Design: Minimizing material usage and optimizing building layout can reduce construction costs. Consider pre-fabricated or modular construction methods for efficiency.
- Negotiating with Suppliers: Negotiating favorable terms with suppliers for materials and services can lower costs. Seeking competitive bids and building strong relationships with suppliers can result in better pricing.
- Value Engineering: This involves analyzing different design alternatives to find the best balance between functionality, quality, and cost. Evaluating and optimizing choices during the design phase can result in significant savings.
- Using Affordable Materials: Choosing suitable alternative materials that meet building codes and quality standards can reduce costs without sacrificing quality.
Return on Investment (ROI) Calculation
Calculating the return on investment (ROI) is essential to assess the project’s financial viability.
ROI = (Net Profit / Cost of Investment) x 100%
Contingency Planning
Contingency planning is essential for managing risks and uncertainties during the project.
- Establishing a Contingency Fund: A dedicated contingency fund should be included in the budget to address unforeseen circumstances. Unexpected challenges, such as material price increases or delays, should be factored into the plan.
- Developing Mitigation Strategies: Develop specific mitigation strategies to address potential risks, such as material price fluctuations or delays in obtaining permits. Having backup plans for unexpected situations can help minimize the impact of unforeseen events.
Comprehensive Project Budget
| Project Phase | Estimated Cost |
|---|---|
| Land Acquisition | $XXX,XXX |
| Design and Permits | $XXX,XXX |
| Construction | $XXX,XXX |
| Interior Finishes | $XXX,XXX |
| Financing Costs | $XXX,XXX |
| Ongoing Maintenance (10 years) | $XXX,XXX |
| Total Estimated Budget | $XXX,XXX |
Construction and Management Strategies
The successful completion of a 24-unit apartment building hinges on well-defined construction and management strategies. These strategies must address the diverse aspects of the project, from selecting appropriate construction methods to ensuring effective tenant relations and building maintenance. Efficient project management, quality control, and a proactive approach to tenant relations are crucial to delivering a high-quality, profitable, and sustainable building.Comprehensive planning and execution are paramount to achieving the desired outcomes.
This includes careful consideration of various construction methods, the selection of reliable contractors and suppliers, and the establishment of robust quality control measures. Effective project management techniques, coupled with a strong tenant relations strategy, will ultimately determine the building’s long-term success.
Construction Methods and Their Impact
Different construction methods offer varying advantages and disadvantages in terms of timelines and costs. Choosing the right method is crucial to project success. Factors like site conditions, budget constraints, and desired building features influence the optimal selection.
| Construction Method | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Construction | Established processes, readily available labor, and familiarity with local regulations. | Potentially higher labor costs, slower construction timelines, and greater risk of delays due to weather. |
| Modular Construction | Faster construction timelines due to prefabrication, reduced on-site labor, and potential cost savings. | Requires specialized equipment and skilled labor, potential for quality issues if not properly managed, and might not be suitable for all building designs. |
| Prefabricated Panel Construction | Faster construction, better quality control, and potentially lower costs compared to traditional construction. | May have limited design flexibility, higher upfront costs for specialized components, and might require specific expertise. |
Potential Contractors and Suppliers
A comprehensive list of potential contractors and suppliers should be developed, including their experience, financial stability, and references. Thorough due diligence is critical to ensuring a reliable and qualified team for the project. Consider firms with a track record of successful apartment building construction and strong relationships with reputable material suppliers.
- Local General Contractors: Companies with experience in similar projects, demonstrated ability to manage complex projects, and a proven track record of timely and quality delivery.
- Specialized Subcontractors: Electricians, plumbers, HVAC technicians, and other specialists with expertise in building systems.
- Material Suppliers: Companies that provide quality building materials at competitive prices.
- Project Management Consultants: Expertise in coordinating all project elements, tracking progress, and managing risks.
Quality Control Throughout Construction
Implementing a robust quality control program is essential to ensure the building meets the required standards and is free from defects. This involves establishing clear quality standards, conducting regular inspections, and addressing any issues promptly. A proactive approach to quality control throughout the entire process minimizes costly rework and ensures customer satisfaction.
- Regular Inspections: Inspections should be conducted at critical stages of the construction process to identify and address any deviations from the approved plans or specifications.
- Quality Assurance Procedures: Implementing standardized procedures for materials handling, workmanship, and equipment use can ensure consistency in quality.
- Testing and Certification: Thorough testing of structural elements, plumbing systems, and electrical systems to guarantee compliance with building codes and safety regulations.
Efficient Project Management Techniques
Implementing effective project management techniques is crucial for timely and cost-effective completion. Techniques such as critical path method (CPM) analysis, Gantt charts, and regular progress meetings can ensure smooth project execution.
- Project Scheduling: Utilizing project management software and techniques like the Critical Path Method (CPM) to determine project timelines and identify potential delays.
- Progress Tracking: Employing tools like Gantt charts to monitor project progress and identify potential bottlenecks.
- Regular Communication: Establishing clear communication channels between the project team, contractors, and stakeholders to address issues proactively.
Tenant Relations and Building Maintenance
A strong tenant relations strategy is critical for building community and fostering a positive experience for residents. Proper building maintenance and responsive service are key to retaining tenants and maintaining property value.
- Tenant Communication: Establishing a communication system for addressing tenant concerns, collecting feedback, and keeping residents informed.
- Building Maintenance Plan: Creating a comprehensive plan for routine maintenance and repairs to ensure the building’s long-term functionality and value.
- Emergency Response System: Developing a clear plan for handling emergencies and addressing tenant needs promptly.
Property Management Strategies
Choosing the right property management strategy is vital for successful operation and profitability. This includes considering the desired level of service, tenant turnover rates, and market conditions.
- Tenant Selection Criteria: Establishing clear criteria for selecting qualified tenants to maintain the desired community and property value.
- Lease Management: Developing a clear lease agreement process to minimize disputes and maintain consistency in tenant relations.
- Financial Management: Implementing a system for collecting rent, managing expenses, and ensuring the building’s financial health.
Final Review
In conclusion, constructing a 24-unit apartment building necessitates a holistic approach that integrates design, site planning, financial projections, and construction strategies. Careful consideration of each phase, from initial design to ongoing maintenance, is vital for a successful project. This comprehensive analysis provides a roadmap for navigating the complexities of such a venture, emphasizing the importance of meticulous planning and execution.
Popular Questions
What are common zoning regulations impacting 24-unit apartment building design?
Zoning regulations vary by location and often dictate building height, density, parking requirements, and setbacks. These regulations must be thoroughly researched and understood to ensure compliance during the design and construction phases.
How can I estimate construction costs for a 24-unit building?
Construction cost estimations involve detailed breakdowns of material costs, labor expenses, permitting fees, and contingency planning. Consult with experienced contractors and construction professionals to accurately gauge these figures.
What are some potential cost-saving measures during the construction phase?
Cost-saving measures include careful material selection, optimizing construction methods, negotiating contracts, and leveraging efficient project management techniques.
What are the essential amenities to include in a 24-unit apartment building?
Essential amenities typically include secure entrances, laundry facilities, adequate parking (if permitted by zoning), and common areas for residents. Amenities should align with the target tenant demographic and market trends.
